inverter in welding machine
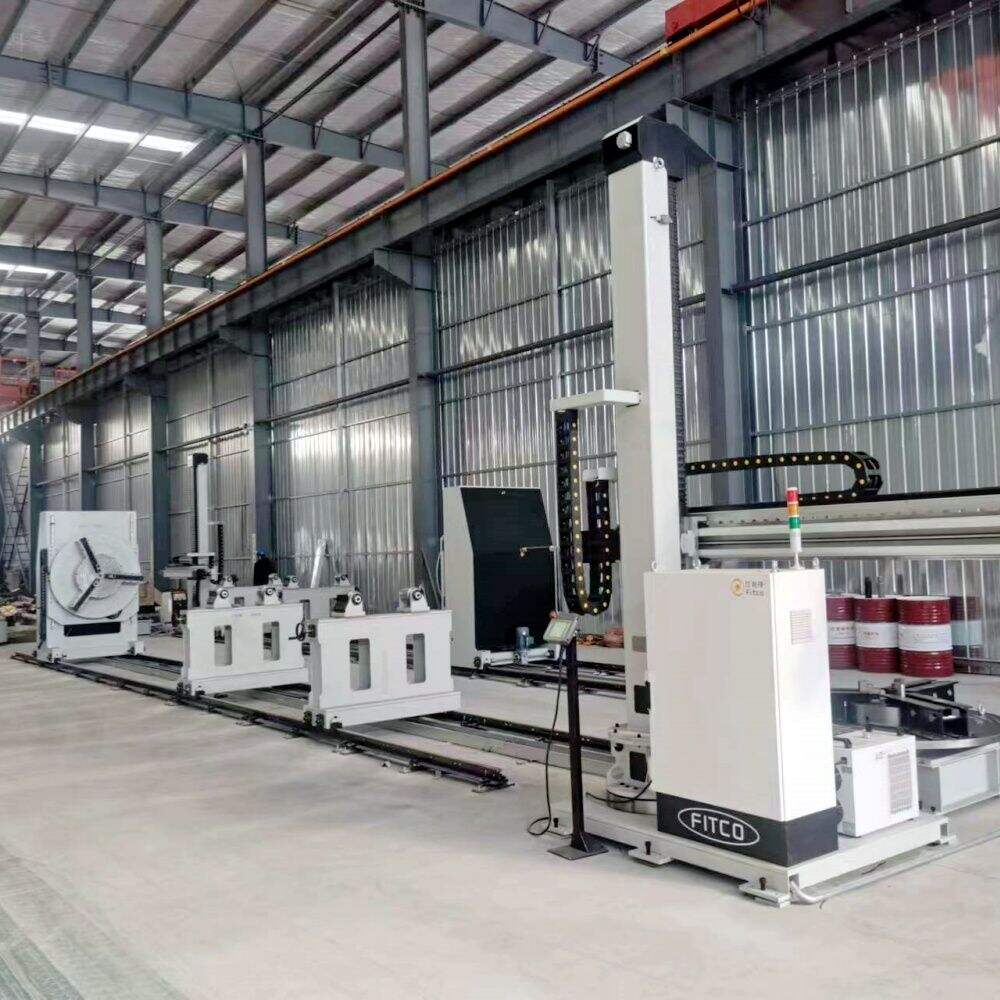
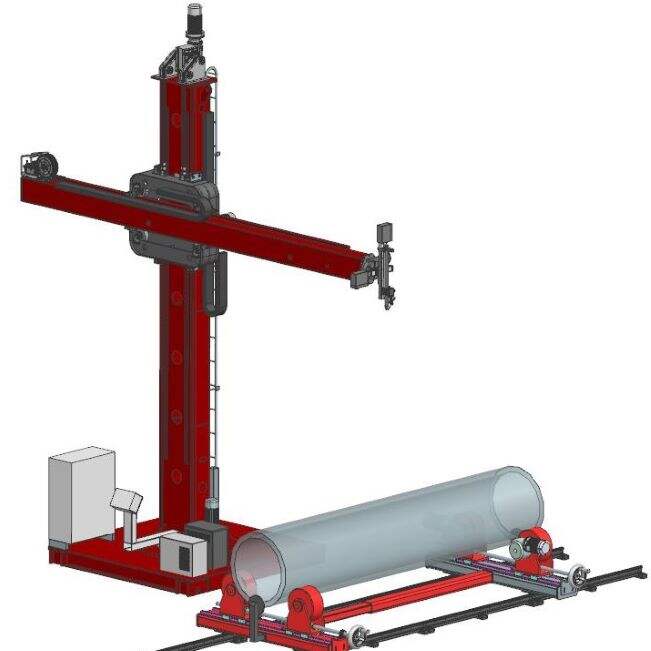
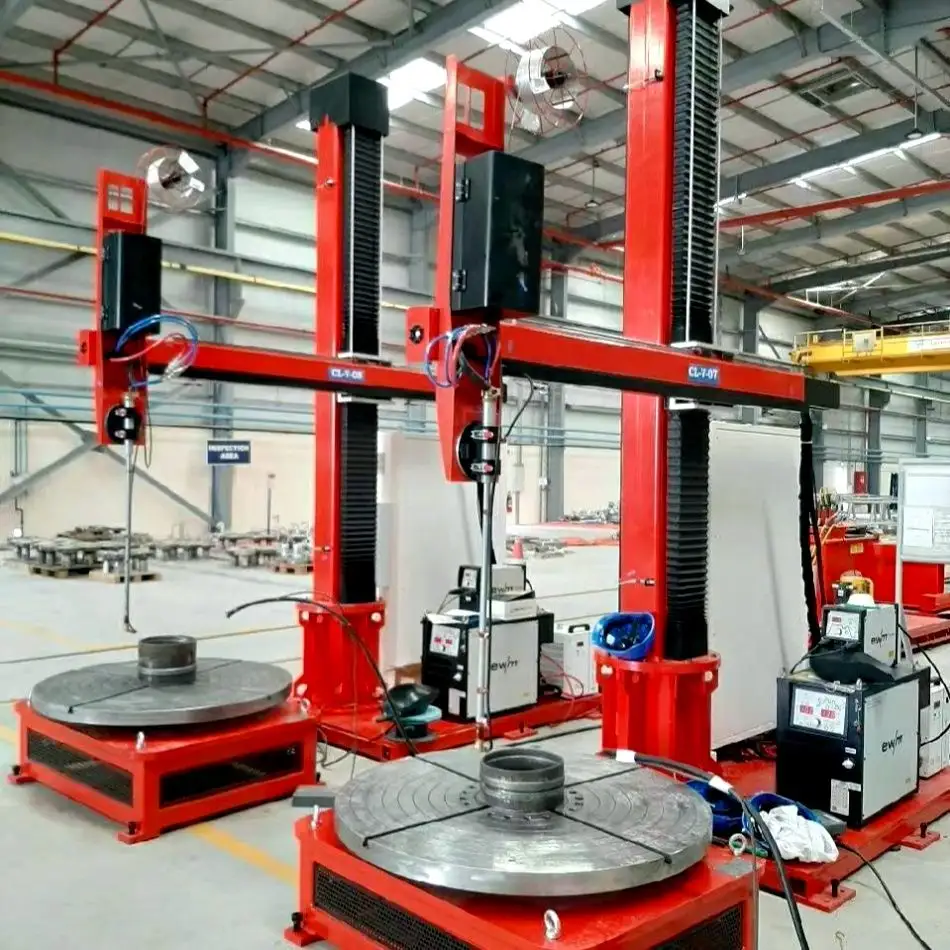
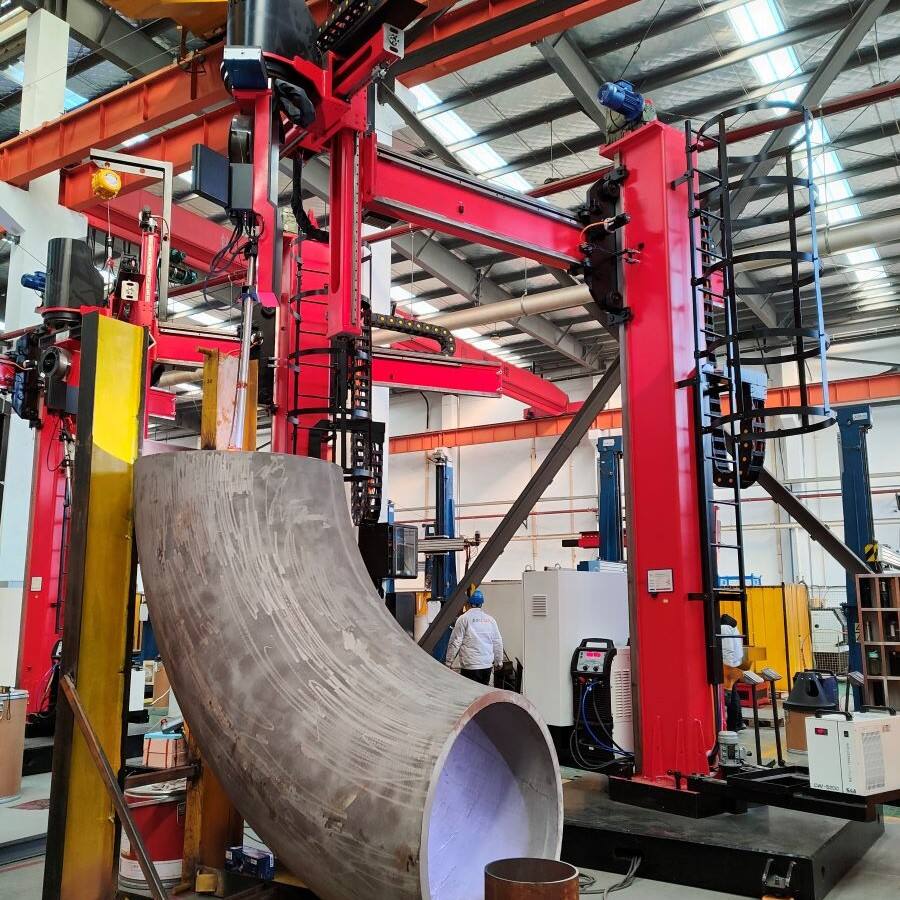
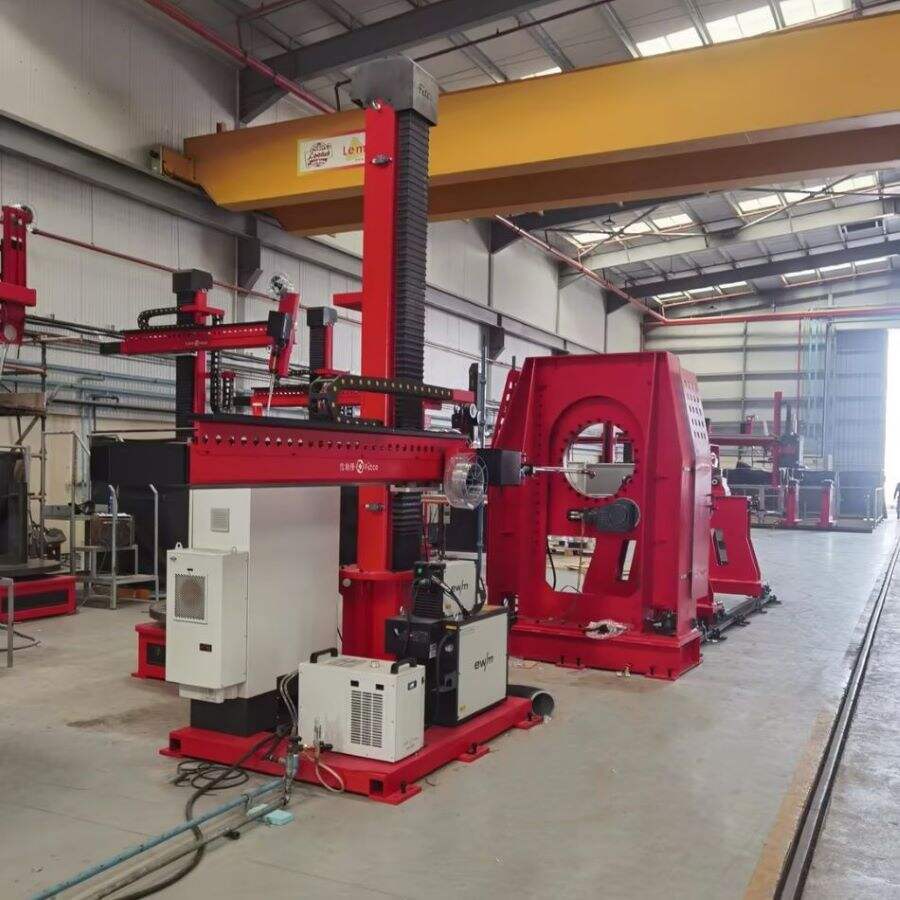
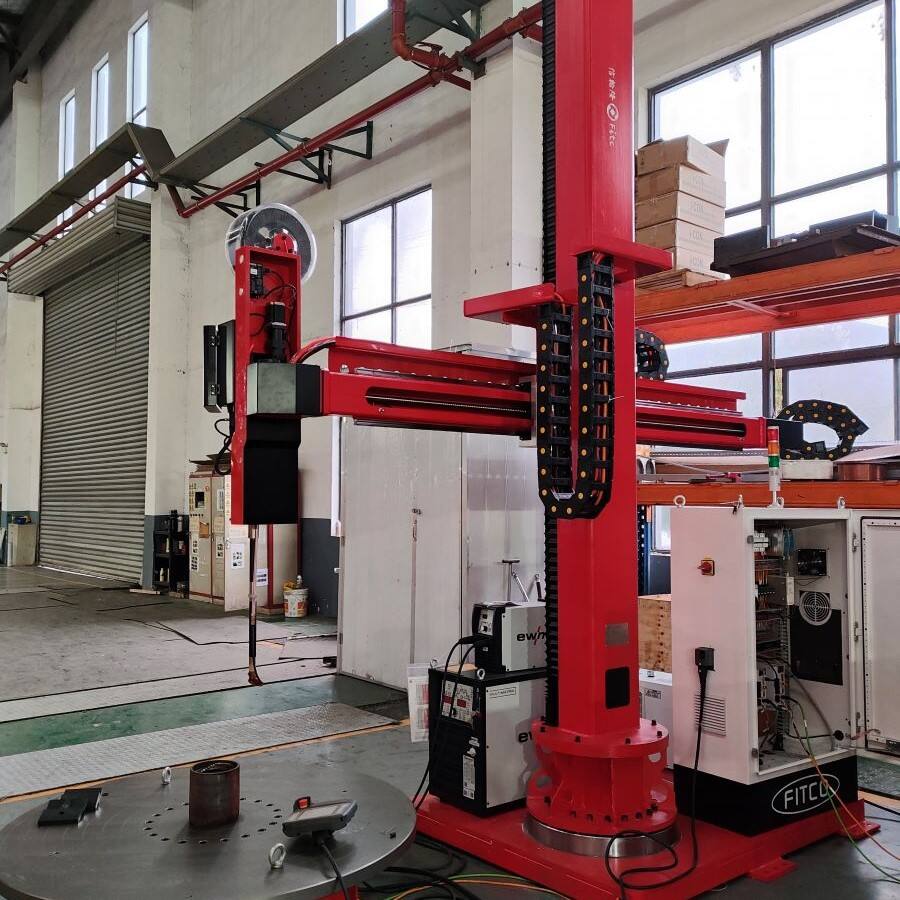
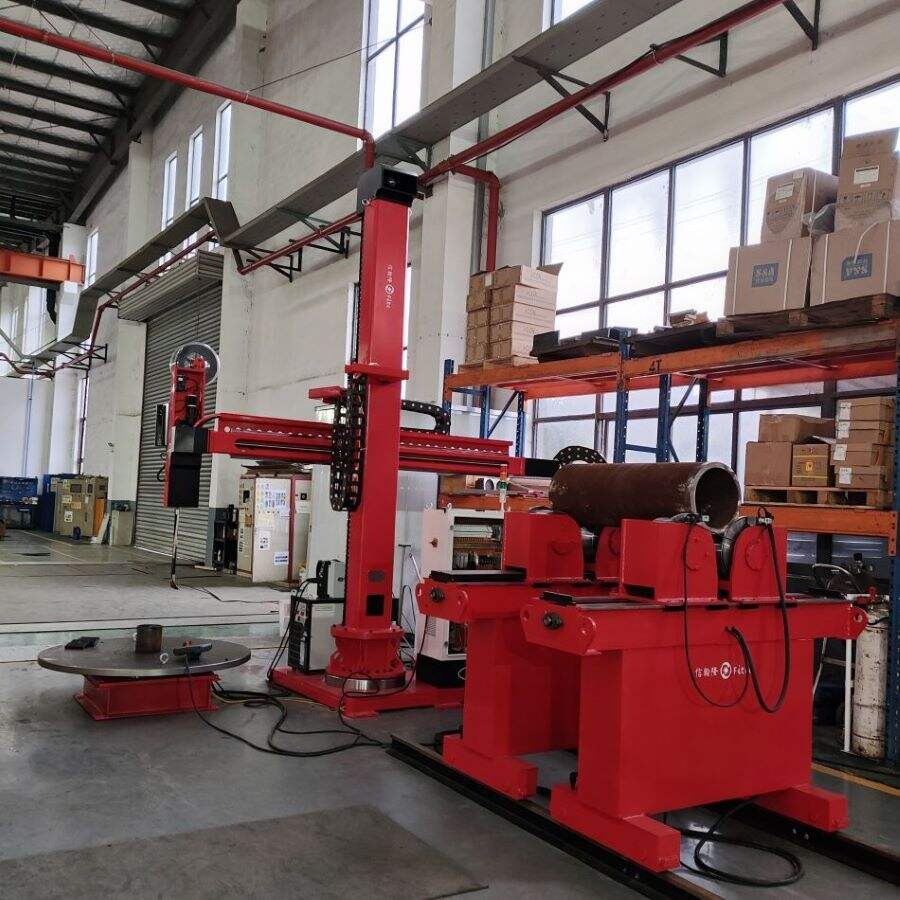
An inverter in a welding machine represents a revolutionary advancement in welding technology, fundamentally transforming how power is managed and delivered during the welding process. This sophisticated electronic component converts standard AC power into high-frequency AC, which is then rectified to DC power, resulting in a more stable and controlled welding arc. The inverter operates by first taking the standard 50/60Hz AC input and converting it to DC. This DC power is then converted to high-frequency AC, typically ranging from 20kHz to 100kHz, before being transformed to the optimal voltage level and rectified back to DC for welding. This process allows for precise control of the welding current and voltage, enabling superior weld quality and consistency. The inverter technology significantly reduces the size and weight of welding machines while improving their energy efficiency. Modern inverter welding machines incorporate sophisticated control systems that can automatically adjust welding parameters in real-time, responding to changes in arc length and material conditions. This advanced capability makes them suitable for a wide range of welding applications, from delicate thin materials to heavy-duty industrial welding tasks.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR BG
BG HR
HR CS
CS DA
DA NL
NL FI
FI FR
FR DE
DE EL
EL HI
HI IT
IT JA
JA KO
KO NO
NO PL
PL PT
PT RO
RO RU
RU ES
ES SV
SV TL
TL IW
IW ID
ID LT
LT UK
UK SQ
SQ HU
HU TH
TH TR
TR FA
FA AF
AF CY
CY MK
MK LA
LA MN
MN KK
KK UZ
UZ KY
KY